- Start
- About the City of Stockholm
- How the City of Stockholm is governed
- Financial operations
- Financial risk management
Financial risk management
The financial policy for the municipal group defines the guidelines and objectives for identifying and managing the financial risks to which the City of Stockholm is exposed.
Examples of financial risks include, but are not limited to, interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, credit risk, financing risk and liquidity risk.
Risk reducing instruments
Risk-mitigating instruments may only be used to eliminate foreign exchange exposure and to manage interest rate risks within the City’s financial operations.
Financing and liquidity risks
The municipal group’s financing risk is managed by spreading debt maturities across several years. The average remaining maturity of the City’s external debt, known as duration, was 1.95 years as of 31 December 2025.
The figure below shows the bond maturity profile for the municipal group.
Share of bond maturities as of 31 December 2025
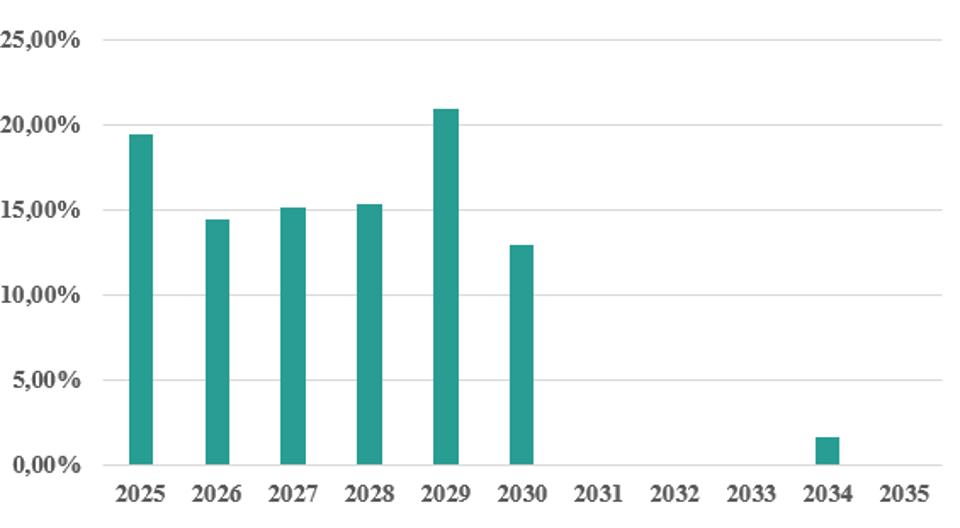
For the year 2026 maturing bonds amount to 8,9 billion SEK. City of Stockholm have a revolving credit facility of 11 billion SEK, and a overdraft facility of 6 billion.
Total readiness for payment amounts to 19,7 billion as of the 31 December 2025.
Credit risks
City of Stockholm’s financial derivative contract exposure is against highly rated international banks and is limited by the framework defined in the financial policy.
Risks as of 31 December 2025
| Municipality group | 31 August 2025 | Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Duration (years) | 1,95 | 1,25–3,75 |
| Interest maturing within 1 year | 43,11 % | max 75 % |
| Dept maturing within 1 year | 17,25 % | max 30 % |
| Payment rediness (B SEK) | 19 740,4 m SEK | min. 10 000 m SEK |
| Credit risk | Within limits | Defined in the Financial policy |
| FX exposure | 0 | max 25 m SEK |
